What is Phishing in Web3?
As users engage in token trading through blockchain transactions, a new form of phishing scam has surfaced. Unlike conventional phishing scams that focus on obtaining personal or financial information from victims, this particular phishing method aims to pilfer users' assets by exploiting transactions. In essence, scammers deceive victims into signing transactions or messages that enable them to withdraw the victims' tokens. In the upcoming sections, we will delve into various prevalent phishing scams in Web3 and acquire practical strategies to safeguard your assets against them.
Prevalent Phishing Scam Types in Web3
1. Direct Token Transfer
This scam manipulates users into directly transferring their assets to malicious addresses. The success of these scams often relies on sophisticated social engineering techniques. A common variant involves deceiving users into signing a transaction under the pretense of a "security update" or a "claim," which ultimately results in the theft of their assets. This type of scam is typically carried out through the utilization of a Fake Interface Scam.
2. Token Approval / Permit
The Approval and Permit methods allow someone else, known as the spender, to utilize your tokens on your behalf. It is a common practice for users to grant token approvals to DApps to facilitate trading activities. However, granting approvals to malicious actors, such as a phishing address, can lead to financial losses. If the victim fails to realize and revoke the approval, a phishing attack can persist for an extended period of time.
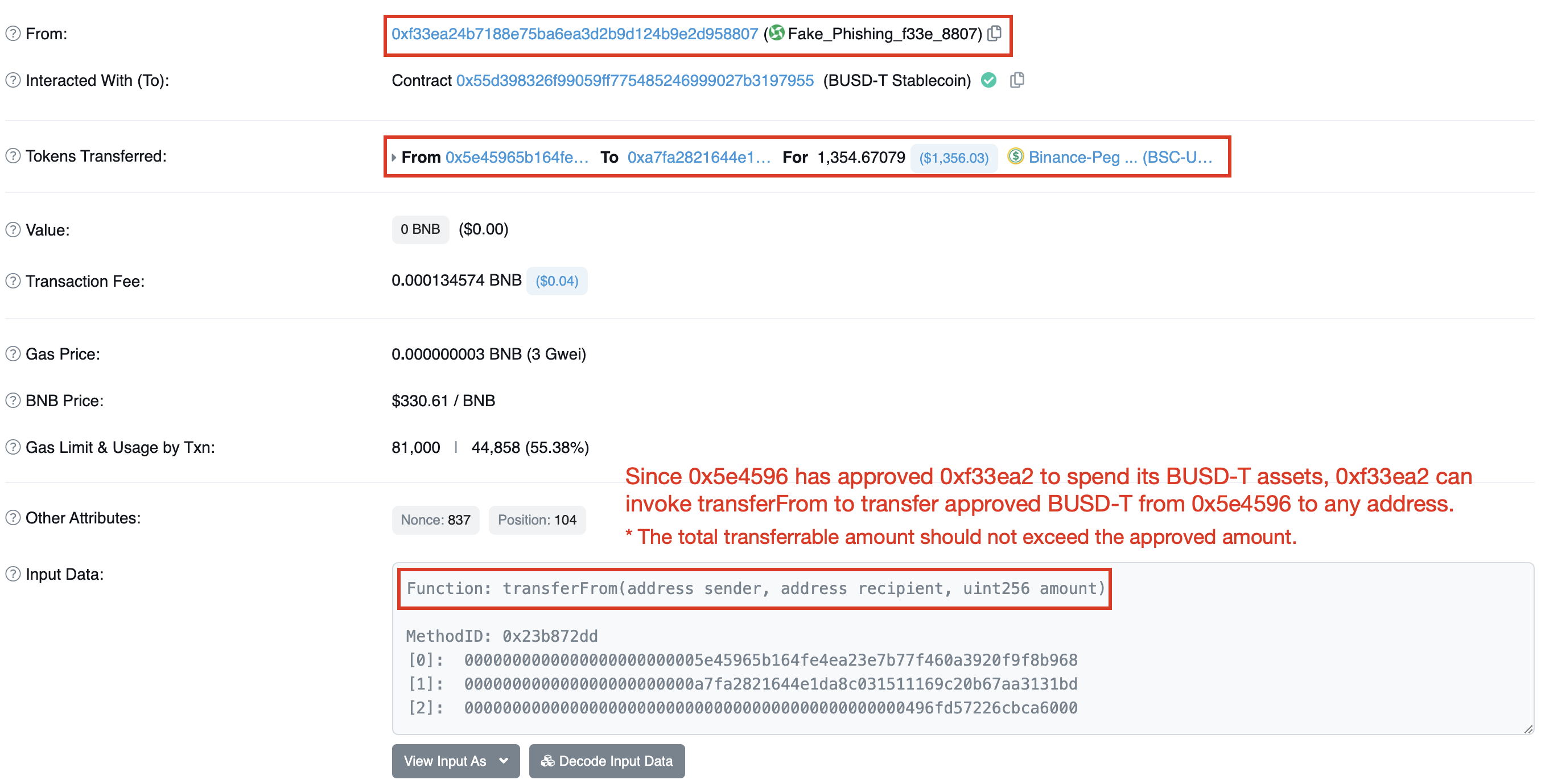
3. Attack transaction example
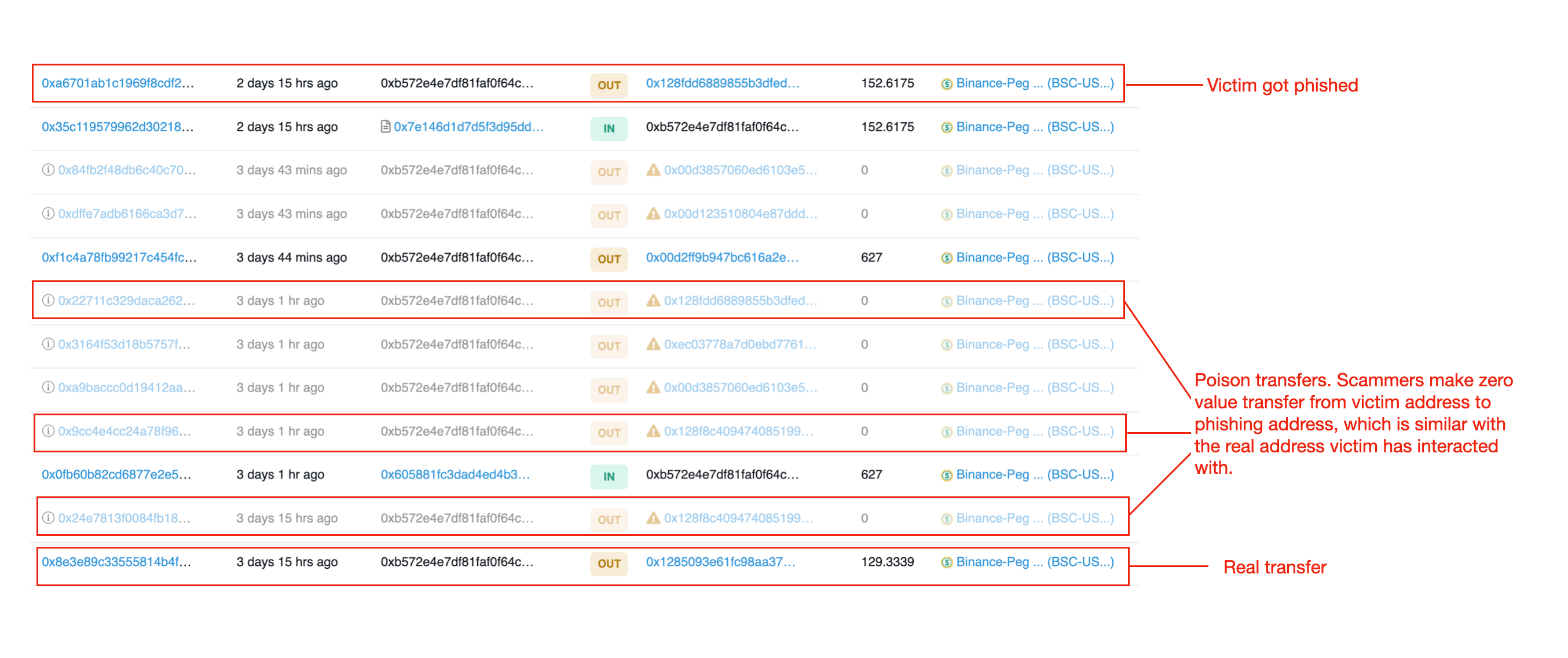
Zero-value transfer scams, also known as "poisoning," occur when phishers manipulate zero-value transfers from a victim's address to a phishing address that resembles the legitimate addresses the victim has previously interacted with. This deceptive tactic aims to trick victims into mistakenly transferring funds to these phishing addresses, resulting in a significant loss of assets.
4. Gas Token Scam
On the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), certain phishers employ airdrop scams, where they distribute fraudulent tokens to victims and persuade them to approve or transfer these tokens. Regrettably, victims unknowingly incur substantial fees when engaging with these scam tokens. These fees are utilized to mint gas tokens to the scammer's address, which are subsequently exchanged for profit.

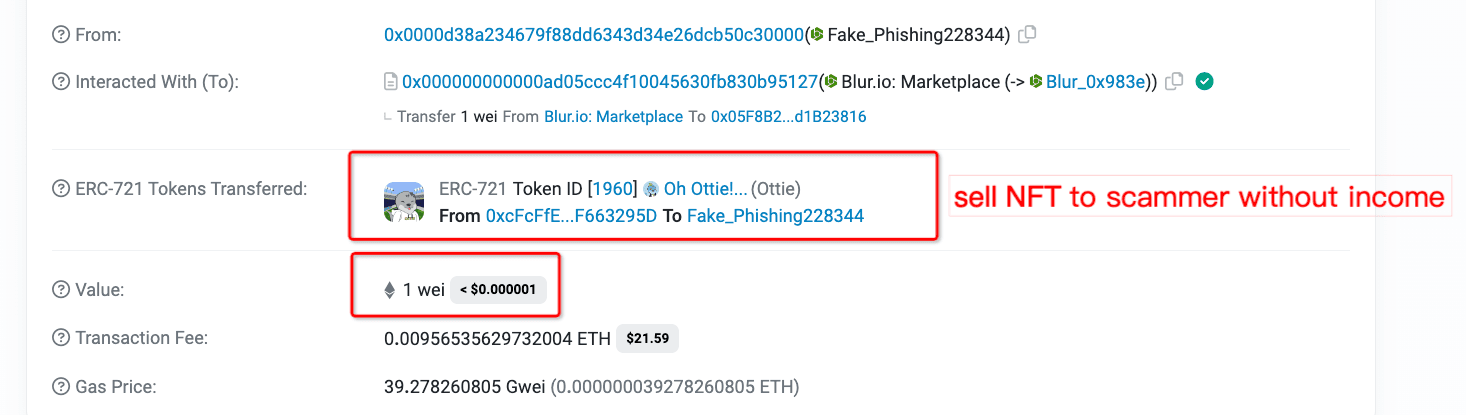
5. NFT Market Scam
NFTs are a unique form of virtual assets. The prices of NFTs from the same collection exhibit significant variation, making automated transactions through decentralized exchanges (Dex) impractical. As a result, the NFT market has emerged, providing a platform for users to place orders and make purchases in a more facilitated manner. However, scammers exploit these markets by creating malicious orders and steal victims' NFTs.
6. Fake Interface Scam
Users interact with on-chain contracts, such as DApps, through contract interface calls. To enhance user understanding, these interfaces are typically presented in the form of method names. However, it's important to note that the method names may not always accurately represent the specific implementation of the method. For instance, a method named "SecurityUpdate" may not necessarily involve a security upgrade but could instead involve the transfer of the caller's assets.


How to Stay Safe from Phishing in Web3
-
Avoid visiting suspicious websites from untrusted sources and be extremely careful with those that require a connected wallet. Many wallets and explorer extensions can alert you to phishing websites. Tools like MetaMask can help.
-
Double-check the addresses you interact with, including EOAs and contracts. Don't assume they are correct just because the first and last few characters of the address are familiar. For addresses you interact with for the first time, use tools to check their risk, such as AvengerDAO's risk scanner and MetaDock.
-
Regularly check and revoke token allowances. Many tools can help you with this. For example, MetaDock is a browser extension that helps users identify risky approvals by improving the token approvals management feature of blockchain explorers.
-
Use multiple wallets and keep your assets distributed. Store only necessary assets in hot wallets for daily use. Keep the vast majority of assets in more secure cold wallets, such as hardware wallets.
About MetaSleuth
MetaSleuth is a comprehensive platform developed by BlockSec to assist users in effectively tracking and investigating all crypto activities. With MetaSleuth, users can easily track funds, visualize fund flows, monitor real-time fund movements, save important information, and collaborate by sharing their findings with others. Currently, we support 13 different blockchains, including Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Tron (TRX), Polygon (MATIC), and more.
Website: https://metasleuth.io/
Twitter: @MetaSleuth
Telegram: https://t.me/MetaSleuthTeam




